Observability is a crucial part of any software product, it helps in
understanding the internal state of a system by collecting and analyzing
metrics, logs, and traces. This information can be used to troubleshoot
issues, identify performance bottlenecks, and make improvements to the
system.
Observability is especially important for complex systems, such as
distributed systems, where it is difficult to track down the root cause of
problems.
There exist several tools out there to help monitor your system's health.
Assuming you have an instrumented system, how could you visualize this
instrumentation information, and get real-time updates on your system
performance?
The topic of observability is divergent and can be spanned across many
posts.
But in this post, I chose one topic that posed a tough challenge to me, and
that is setting up the APM Server of Elasticsearch, given how scattered
their documentation is, and the lack of community support, the challenge was
real, hopefully for someone trying to fi I'm going to set up the Elastic APM
Server, one of the popular tools to analyze metrics.
Let's get straight to it...
Setting up Elasticsearch
docker run --name es01 --net elastic -p 9200:9200 -it -m 1GB docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.10.4ToFor information, please refer to:
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/docker.html#_start_a_single_node_cluster
Run this command, and make sure the container es01 is running:
docker ps
For Rancher Desktop Users
If you are using Rancher Desktop instead of Docker Desktop, you might face
this problem:
If the container has stopped unexpectedly (please use
docker logs es01 to
inspect the reason), you may see this error:
node validation exception\n[1] bootstrap checks failed.
You must address the points described in the following [1] lines before starting Elasticsearch.\n
bootstrap check failure [1] of [1]: max virtual memory areas vm.max_map_count [65530] is too low, increase to at least [262144]", "ecs.version"
For information, please see
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/elasticsearch/reference/current/vm-max-map-count.html#vm-max-map-count
To fix, enter Rancher Desktop shell:
rdctl shell
Then run this command:
sysctl -w vm.max_map_count=262144
To exit the shell, run:
exit
Then restart Rancher Desktop (make sure Rancher Desktop GUI is activated):
rdctl shutdown
Then restart Rancher Desktop (make sure Rancher Desktop GUI is activated):
rdctl shutdown
rdctl start
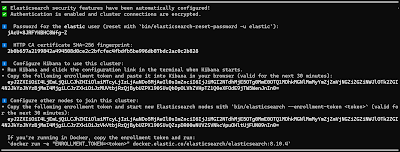
Take note of the 'elastic' user password, the enrollment token for Kibana, and
the SHA-256 fingerprint of the CA certificate, that are being printed to the
terminal (I found the output to be malformed when I previewed the logs from
text-based editors):
The password is for the 'elastic' user and you can use it to login to Kibana.
You can regenerate it using this command:
docker exec -it es01 /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic
The enrollment token is used to setup the user authentication when setting
up Kibana for the first time.
You can regenerate it using this command:
docker exec -it es01 /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana
Since we are setting a single-node cluster, we are not interested in the
other enrollment token.
The SHA-256 fingerprint of the CA is used with services that needs to
identify the CA of Elasticsearch when they establish the HTTP connection.
You can get it through this command:
docker exec es01 openssl x509 -fingerprint -sha256 -in config/certs/http_ca.crt
Make sure to remove the colon ":" from the fingerprint and convert it to
lowercase:
PS
C:\Users\melshawaf> "71:5E:E2:EB:FE:42:70:26:C6:09:50:68:3E:F2:4F:48:C9:C3:09:65:F6:F4:39:77:59:2D:31:80:E7:6C:34:62".Replace(":","").ToLower()Setting up Kibana
Create Kibana docker container:
docker run --name kib01 --net elastic -p 5601:5601 docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:8.10.4For more information, please refer to
💡 If you found the Kibana setup stuck at the "Complete setup" step, just refresh the browser.
APM
Architecture
From the official documentation, this is how the ELK Stack comes together
for the data to flow from the client application to Kibana.
For more details on how the integration work, please refer to the official
documentation
Using the Elastic APM Agent is the recommended approach.
💡The OpenTelemetry bridge is part of the core agent package (Elastic.Apm), so you don’t need to add an additional dependency.
Setting up
You can either download the binaries and run them on the hosting machines
(self-managed), or use the Docker images. I will use Docker for
Elasticsearch and Kibana, and install the APM Server on the hosting machine.
-
Download APM Server
Use this link to download APM Server: https://www.elastic.co/downloads/apm
Then extract the content into C:/Program Files/APM-Server where the APM-Server folder contains the apm-server.yml file. -
Create the roles for the APM Server user
We will use APM Server to send diagnostics data to Elasticsearch then we can view these data from Kibana, but first we need to grant APM Server the required privileges, to be able to call Elasticsearch's APIs.
Use Kibana dev tools to create the user which will represent the APM Server and its roles:
You can access the dev tool console from this link: http://localhost:5601/app/dev_tools#/console -
write_apm role
POST /_security/role/write_apm { "cluster": ["all"], "indices": [ { "names": ["apm-*", "traces-apm*", "logs-apm*", "metrics-apm*"], "privileges": ["auto_configure","create_index", "view_index_metadata", "create_doc"] } ] } -
read_apm role
POST /_security/role/read_apm { "indices": [ { "names": ["apm-*", "traces-apm*", "logs-apm*", "metrics-apm*"], "privileges": ["read", "view_index_metadata"] } ] } -
apm_admin user
POST /_security/user/apm_admin { "password" : "asdfjkl", "roles" : [ "read_apm", "write_apm", "kibana_admin"], "full_name" : "APM Metrices" } -
Configuring APM Server
Open apm-server.yml file, and make the following changes:
-
apm-server.auth.secret_token: "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6Ikpva"
you can generate this token yourself, it's used by the APM Server and the agent, I didn't find a documentation on where to generate it, so I assumed it's left to the user to generate it. -
The username with appropriate roles to read/write APM data.output.elasticsearch.hosts.username: "apm_admin" -
The password of the user currently using APM.output.elasticsearch.hosts.password: "asdfjkl"
Before using APM Server, you will need to install the CA certificate on
your host machine, let's install it:
-
Copy the CA certificate to a local folder
docker cp es01:/usr/share/elasticsearch/config/certs/http_ca.crt C:/Certs - Install it on the local machine to the Trusted Root Certification Authorities store.
You can either install the service (using the provided script in
the installation folder) or run it directly from the command line:
PS C:\Program Files\APM-Server> ./apm-server.exe -eAdding APM Integration in Kibana
Find APM integration, from Elastic APM in Fleet tab, Add
APM integration.
Leave the defaults and save. You will be prompted to add an elastic Agent,
we will use the .NET agent.
Configuring the .NET APM Agent and running a sample app
Add the NuGet package per your needs, there are many of them:
depending on what part of your app you want to instrument.
You can use Elastic.Apm.NetCoreAll package that adds every agent
component to your application.
Let's create a simple application, just to see something in Kibana...
-
Install Elastic.Apm.NetCoreAll package, add this to the main
CSProj:
<PackageReference Include="Elastic.Apm.NetCoreAll" Version="1.25.0" /> -
Add the middleware:
app.UseAllElasticApm(builder.Configuration); -
Configure the APM Agent in the appsettings.json:
"ElasticApm": { "ServiceName": "My-Instrumented-App", "SecretToken": "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9.eyJzdWIiOiIxMjM0NTY3ODkwIiwibmFtZSI6Ikpva", "ServerUrl": "http://localhost:8200", "Environment": "DEV" } -
In a background service run a recurring task that, for example, does
this:
private async Task AnalyzeMessage(Dictionary<string, object> attributes) { using var activity = _activitySource.StartActivity("AnalyzeMessage"); // Let's pretend a logn-time operation is being processed here... await Task.Delay(1000); await CountAttributes(attributes); activity.DisplayName = "Analyzing message"; activity?.SetTag("First attribute", attributes.First().Value); activity?.SetTag("Last attribute", attributes.Last().Value); } -
Run the app, you should see a service called "My-Instrumented-App"
in APM>Services in Kibana:

Fleet
For a single node installation, we probably don't need to use Fleet, please
have a look at this discussion
Useful Elasticsearch queries
I found those queries to be useful when working on APM Server:
-
If you want to delete a service from the APM> Services view in
Kibana, you need to delete the associated indices.
POST .*apm*/_delete_by_query { "query": { "term": { "service.name": { "value": "My-Instrumented-App" } } } - To be able to delete multiple indices with one operation (using wildcards), you need to set "action.destructive_requires_name" to false:
PUT _cluster/settings { "transient": { "action.destructive_requires_name": false // allow wildcards } }
Finale!
That brings us to the end of the post, if you followed along then you now have an instrumented app that publishes its traces to Elasticsearch and view these traces in Kibana.
Do you have custom metrics you want to visualize in Kibana?
Unfortunately APM Server doesn't support custom metrics, you will need to set up Metricbeat, and that is the topic of the next post, see you there!






No comments:
Post a Comment
Note: Only a member of this blog may post a comment.